Describe How New Nucleotides Are Added During Dna Replication.
Recall that adenine nucleotides pair with thymine nucleotides and cytosine with guanine. Each daughter strand contains one old strand and one new strand.
The DNA strands separate and complementary nucelotides are added to each strand describe the role of helicases and DNA polymerases during DNA replication DNA helicases catalyze the break up of the hydrogen bonds between strands.
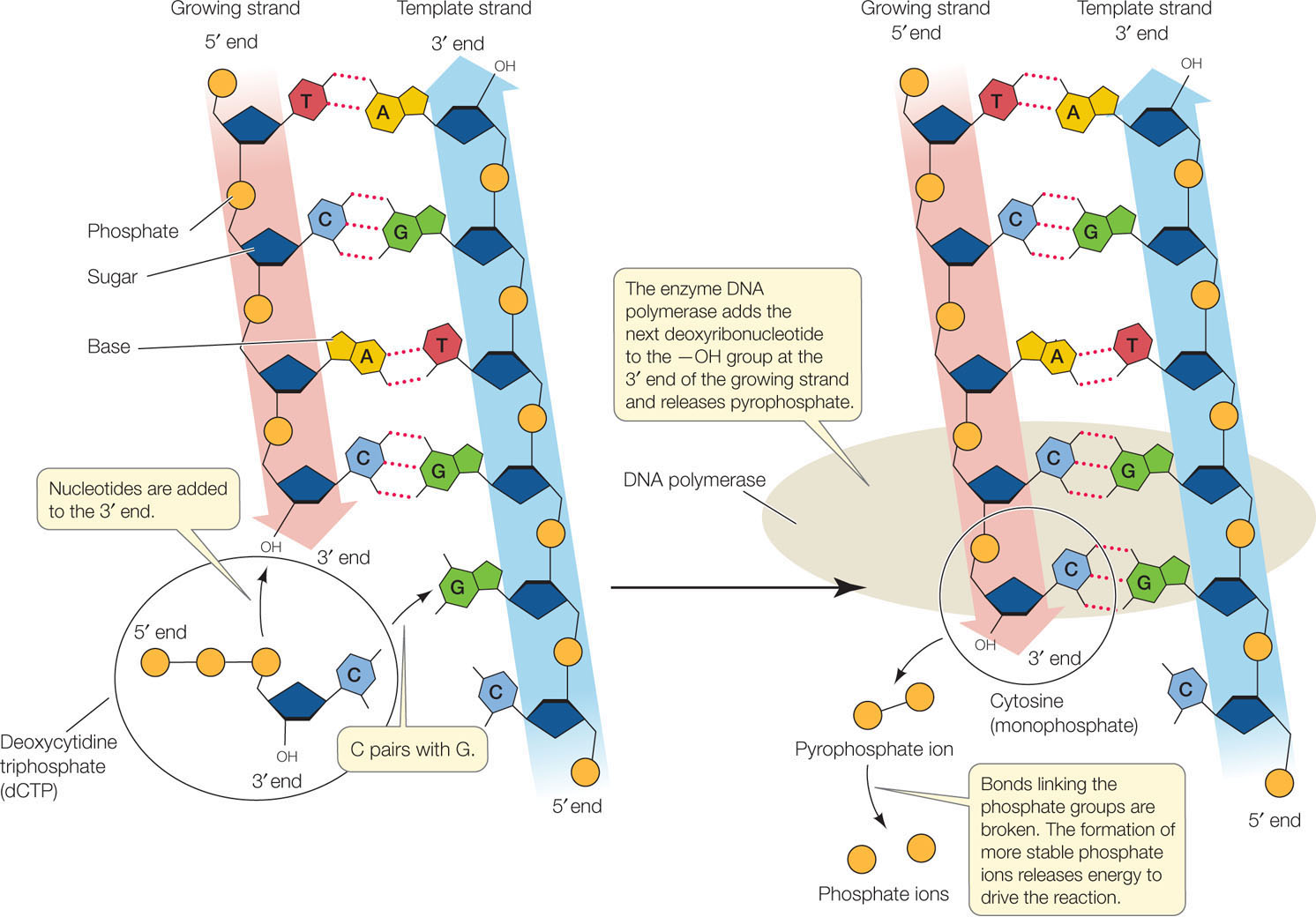
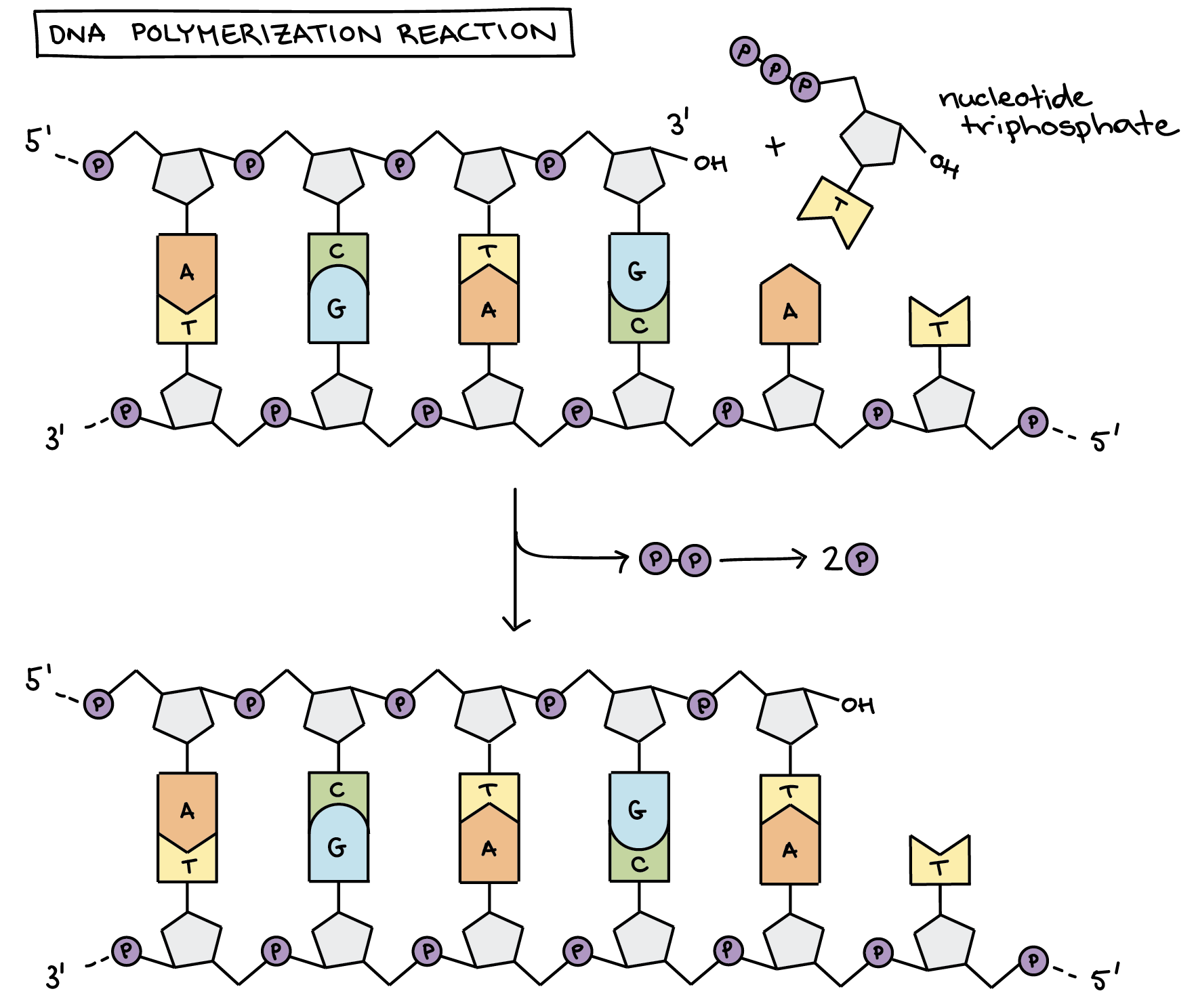
. DNA polymerase slipping results from the presence of the trinucleotide repeat. DNA polymerase adds a new strand of DNA by extending the 3 end of an existing nucleotide chain adding new nucleotides matched to the template strand one at a time via the creation of phosphodiester bonds. This exposed the bases that are typically the rungs of the double helix.
First the double helix is unzipped using DNA helicase. The nucleotides used in replication contain old and new. A hairpin forms when helicase unwinds the double strand.
Initiation at the origin of replication unwinding to expose the strands synthesis on both strands with many enzymes adding nucleotides 3 to 5. Which of the following correctly explains why DNA replication is described as semiconservative. Leading strand synthesis occurs continuously.
Video is an animated explanation of How Nucleotides are Added in DNA Replication. DNA polymerase slippage results from the presence of a hairpin. Second now that the bases are open DNA polymerase will bring new nucleotides.
New bases are added to the complementary parental strands. DNA polymerase slippage results from the presence of a hairpin. This addition is continuous in the leading strand and fragmented in the lagging strand.
Bases form pairs base pairs in a very specific way. The elucidation of the structure of the double helix provided a hint as to how DNA is copied. A hairpin forms when DNA polymerase adds new nucleotides.
The bases are matched according to base pair rules - Adenine. In each new DNA double helix one strand is from the original molecule and one strand is new. During DNA replication new nucleotides are added at the 3 end of the molecule.
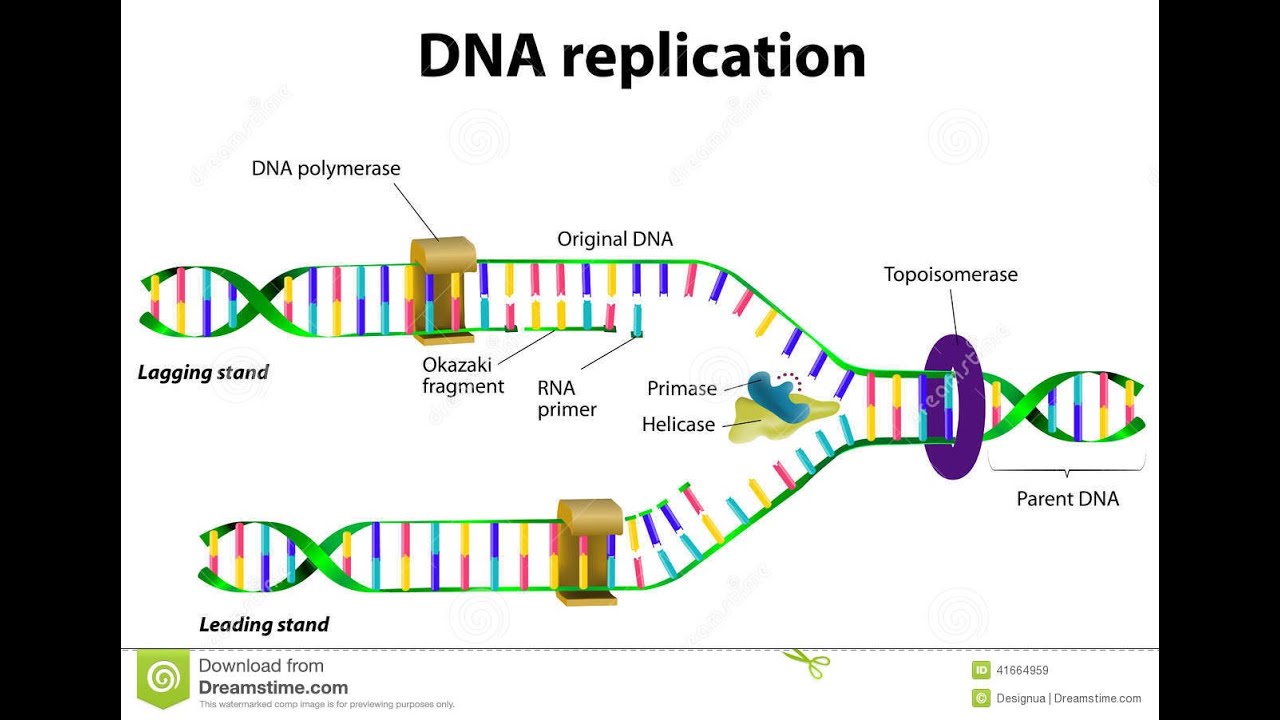
DNA polymerases add complementary nucleotides Describe the role of helicases and DNA polymerases during DNA replication. An active zone of DNA replication moves progressively along a replicating DNA molecule creating a Y-shaped DNA structure known as a replication fork. Where on the deoxyribose component are new nucleotides added during DNA.
DNA replication occurs in a series of five steps. DNA replication is an essential part of cell division as it ensures that each new cell has the same genetic information. The trinucleotide regions are replicated during two rounds of replication but will not be replicated again once round two is completed DNA polymerase slipping results from the presence of the trinucleotide repeat.
It is also necessary for evolution and immune system response. A hairpin forms when DNA polymerase adds new nucleotides. Select all statements that describe the process correctly.
Be able to describe the chemical bonds involved in the holding the deoxyribose. Specific base pairing in DNA is the key to copying the DNA. If you know the sequence of one strand you can use base pairing rules to build the other strand.
Because DNA polymerase can only add new nucleotides at the end of a backbone a primer sequence which provides this starting point is. This means that one strand has a series of breaks in the sequence. Each of the new DNA molecules has conserved one of the two original DNA strands.
Okazaki fragments remain in the DNA. A primer is needed to start replication. DNA Replication Study Guide study guide for dna replication lecture know the structure of double stranded dna.
The nucleotides used in replication are recycled multiple times. Figure 8 shows how A adenine pairs with T thymine and G guanine pairs with C cytosine. Lagging strand synthesis occurs in the same direction as the replication fork.
Upgrade to remove ads. Each daughter strand contains two new strands. During elongation an enzyme called DNA polymerase adds DNA nucleotides to the 3 end of the template.
Biology Chapter 12 DNA. Leading strand is synthesised continuously. DNA unwinds at the origin of replication.
One new strand is made continuously while the other strand is made in pieces. During DNA replication trinucleotides can be added to the DNA strand. The synthesis of the new strands requires a primer a short RNA strand to which new nucleotides are attached.
DNA polymerases add complementary nucleotides state why DNA replication is a semi-conservative process. DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the deoxyribose 3 ended strand. DNA STRUCTURE AND REPLICATION REVIEW.
DNA replication is a multistep process where new DNA is made. The trinucleotide regions are replicated during two rounds of replication but will not be replicated again once round two is completed. A replication fork is formed which serves as a template for replication.
Primers are removed new DNA nucleotides are put in place of the primers and the backbone is sealed by DNA ligase. Primers bind to the DNA and DNA polymerases add new nucleotide sequences in the 5 to 3 direction. DNA replication begins at the replication fork where the DNA is unwound and each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new strand.
Prior to replication the DNA uncoils and strands separate. DNA polymerase will add the free DNA nucleotides using complementary base pairing A-T and C-G to the 3 end of the primer this will allow the new DNA strand to. Strands are polymers of nucleotides.
The synthesis of the new strand occurs in the 5-3 direction. The two arms of each Y Initially the simplest mechanism of DNA replication seemed to be the continuous growth of both new strands nucleotide by nucleotide at the replication fork as it moves from one end of a DNA molecule to. This happens in a 5 to 3.
The replication of DNA occurs during the synthesis phase or S phase of the cell cycle before the cell enters mitosis or meiosis. The trinucleotide regions are replicated during two rounds of replication but will not be replicated again once round two is completed.

Molecular Events Of Dna Replication Learn Science At Scitable
No comments for "Describe How New Nucleotides Are Added During Dna Replication."
Post a Comment