Define Economies of Scale and Explain Why They Might Arise
Economics questions and answers. Define economies of scale and explain why they might arise.
Economies Of Scale Definition Types Effects Of Economies Of Scale
Economics questions and answers.
. Solution for Define economies of scale and explain why they might arise. Define economies of scale and explain why they might arise. Economies of Scale.
Economies of scale often arise because higher production levels allow specialization among workers which permits each worker to become. Define diseconomies of scale and explain why they might arise. Define diseconomies of scale and explain why they might arise.
What is an example. Define economies of scale and explain why they might arise. Explain the relationship between total product marginal product and average product.
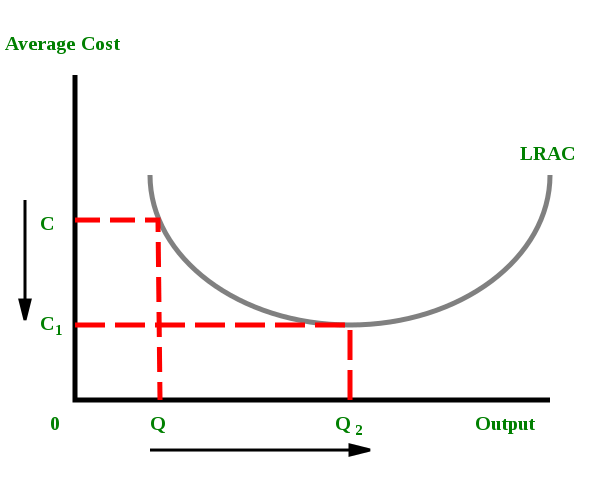
What is an example. Want to see the step-by. The greater the quantity of a good produced the lower the per-unit fixed cost because these costs are shared over a larger number of goods.
Economies of scale might arise due to the reason of rapid growth of supporting industries and also due to tax breaks. Define economies of scale and explain why they might arise. As producion volumes increase with additions of capacity the unit cost to produce a product decreases to an optimal level Define diseconomies of scale and explain why they might arise.
Economics eco-310-01 Workshop Three - 34 Questions Problems_Applications - Chapter 12 P 251 Question 1 What is the relationship between a firms total rev enue profit Define economies ofscale and explain why they might arise. How does fixed cost affect marginal cost. Economies of scale can be both internal managerial advantagesetc and external technological advancement financial advantagesetc Economies of scale arises mainly because of the inverse relationship between quantity produced and per.
Economies of scale are an inverse relationship between fixed price and quantities produced. Define diseconomies of scale and explain why they might arise. As more and more quantities are produced the production level rises and this allows specialization among workers as a result each worker becomes better and better at.
Define economies of scale and explain why they might arise. Explain the relationship between total product marginal product and average. Economies of scale.
Also draw the long run average total cost curve to explain the economies and diseconomies of scale. The advantage arises due to the inverse relationship between per-unit fixed cost and the quantity produced. Define diseconomies of scale and explain why they might arise.
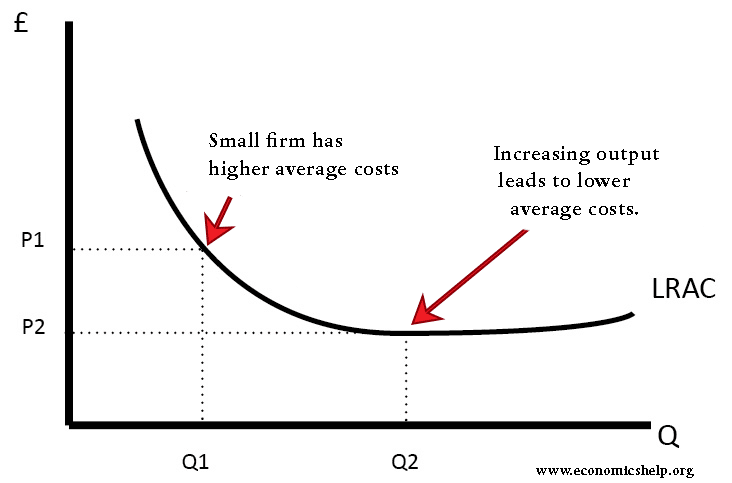
100 8 ratings for this solution. Diseconomies of scale exist when long-run average total cost rises as the quantity of output increases which occurs because of coordination problems inherent in a large organization. Companies can achieve economies of scale by.
Define diseconomies of scale and explain why they might arise. Economies of scale are cost advantages reaped by companies when production becomes efficient. The property whereby long - run average total cost falls as the quantity of output increases.
First week only 499. Economies of scale exist when long-run average total cost falls as the quantity of output increases which occurs because of specialization among workers. As the quantity increases the.
An example of economies of scale is the rise in the purchasing power of firm and the financial economies of scale. Chapter 13 Problem 8QR is solved. A Define economies of scale and explain why they might arise.
Define diseconomies of scale and explain why they might arise. Define diseconomies of scale and explain why they might arise. With this principle.
Define economies of scale and explain why they might arise. Define economies of scale and explain why they might arise. Economies of scale arise due to the inverse relationship between average fixed cost and quantity.
The greater the quantity of a good produced the lower the per-unit fixed cost because these costs are shared over a larger number of goods. Please help this is for microeconomics. Economies of scale are the inverse relationship between quantities produced and fixed price.
Economics questions and answers. Define diseconomies of scale and explain why they might arise. Define economies of scale and explain why they might arise.
Start your trial now. Define economies of scale and explain why they might arise. Define diseconomies of scale and explain why they might arise.
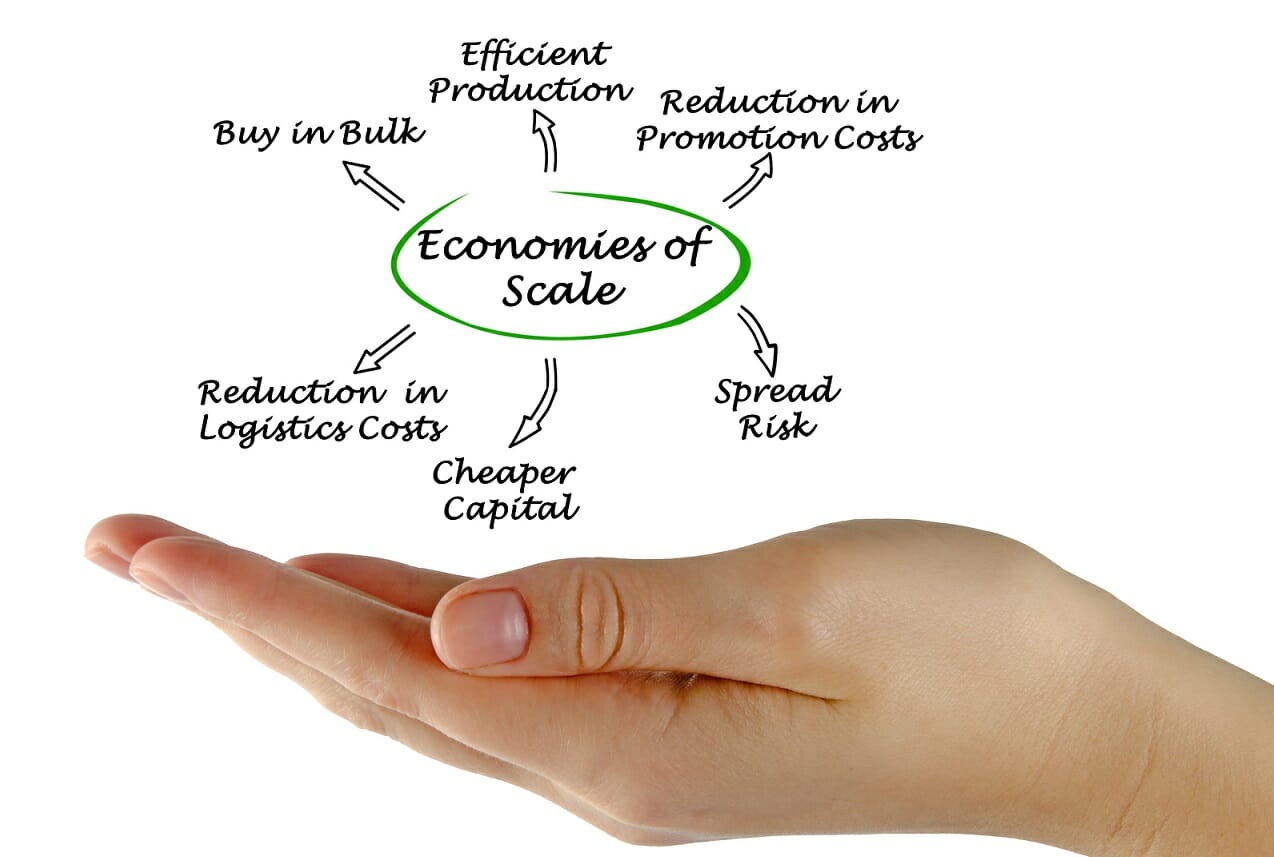
What are Economies of Scale. Essentials of Economics 8th Edition Edit edition Solutions for Chapter 12 Problem 8QR. Economic scale is the reduction of cost per unit that results in an increase in production and this is a result firms efficiency.
B Show the relationship between Marginal cost and Average total cost curve for a typical firm. This refers to the reduction of costs by a firm as a result of increase in the output level of the firm. Define diseconomies of scale and explain why they might arise.
Economies of scale refer to the cost advantage experienced by a firm when it increases its level of output. They may be caused by increased specialization among workers as the factory get. It takes place when economies of scale no longer function for a firm.
Define economies of scale and explain why they might arise. Reduction in long run average and marginal costs due to increase in the operating capacity of a firm. Define economies of scale and explain why they might arise.
It can be caused by increased specialization among workers as a factory gets larger. Define economies of scale and explain why they might arise. Please help this is for microeconomics.
Define diseconomies of scale and explain why they might arise. Diseconomies of scale happen when a company or business grows so large that the costs per unit increase. They arise because of the relationship between the fixed cost and quantity.
Define economies of scale and explain why they might arise. Economics of scale is when the productivity of an industry rises as the production increases.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/diseconomies_of_scale_final-db85c494049d42aca10deb37e214a013.png)
Diseconomies Of Scale Definition
Economies Of Scale Definition Types Effects Of Economies Of Scale
No comments for "Define Economies of Scale and Explain Why They Might Arise"
Post a Comment